When it comes to diagnosing your car’s problems, you should understand the P-codes, or generic fault codes, and know what to do if you encounter them. These codes are defined in the EOBD / OBD-II standard, but manufacturers can also add their own codes and create manufacturer-specific definitions.
Generally speaking, generic codes begin with P0 while manufacturer-specific codes start with P1. There are also additional code groups and sets that expand your code list.
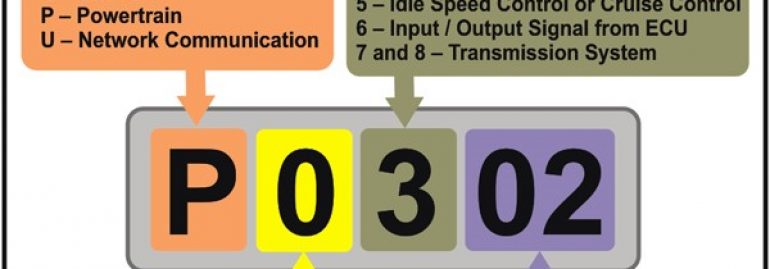
P-codes
While the majority of OBD-II fault codes are generic in nature, there are also specific codes for specific car manufacturers. The first digit in the code tells you whether the fault is manufacturer-specific or generic. Manufacturer-specific codes include the first digit “1” and are usually assigned to faults involving emissions systems. If you have a problem with your car’s emissions system, a generic code might be the culprit.
The first digit of a P-code indicates which specific sensor the car has malfunctioned. The P-code is then followed by a letter (A-F) containing the second digit. These codes are defined in the OBD II network and can be read by a technician. Do-it-yourselfers can also attempt to diagnose the problem by identifying the P-codes themselves.
DTCs can be categorized by manufacturer, function, or location. The body and chassis codes cover features inside the passenger compartment. C-codes describe functions outside the passenger compartment, such as the engine, transmission, and associated drivetrain accessories. U-codes are more general and are used to diagnose problems with network and vehicle integration systems. If you do not recognize the code, consult your owner’s manual or the manual of your car. There are even software tools designed to simplify the process.
The engine code is also called a standard code. It is the first type of code to appear on the display. Usually, it indicates a problem in the engine. Other codes report problems in the emissions system or the engine. While standard codes indicate problems in the engine, pending codes report abnormal behavior and aren’t turned on by the check engine light. However, they are still worth investigating since they are indicative of an underlying issue.
The P0128 code indicates an issue with the fuel and air metering subsystem. P0128 is a generic fault code and isn’t manufacturer-specific. It is standardized and can be interpreted according to SAE definitions. This error code indicates an engine or drivetrain problem. Further, P0229 indicates a problem with the fuel and air metering subsystem. In this case, it is best to contact a mechanic.
Most newer vehicles use the same diagnostic connector. The hardware and software for P-codes is similar across most vehicles. In order to read DTC fault codes, you must have a 16-pin diagnostic connector. Some models are hidden behind the dashboard, but you can always consult the owners manual to locate the OBD-II diagnostic connector on your vehicle. Once you locate it, you can begin the diagnostic process.
If the temperature is constantly above a certain point, you may need to perform a diagnostic test. You can also perform an emission test to check for the codes. Some cars can have more than one P-code. The diagnostic process for an ECU is similar to that of an engine. The ECU uses the P-code to indicate the malfunction. If the problem is the same for both engines, it is highly likely to be an engine issue.
P0430
If you have a car with a P0430 generic fault code, there are a few things you can do to get the car back on track. If the code is caused by a faulty sensor, you should contact a mechanic. Depending on your needs, you may be able to diagnose the problem yourself with a simple diagnostic check, but if you’d like to go the extra mile, you may want to consider a professional automotive mechanic. Whether you want to repair your car yourself or pay a mechanic to help you, there are a variety of ways to fix it, including getting the code and reading the faulty sensor.
First, check the catalytic converter. If it’s showing the code, the converter has stopped working properly. The catalytic converter is responsible for breaking down the pollutants produced by the engine. Without it, the vehicle will emit a higher level of smog than usual, which may mean a failed state emissions test. If this code is present, it’s wise to take your car to a shop that has a catalytic converter cleaner.
There are other possible causes for the code. Whether your car’s catalytic converter is faulty, or you have a defective oxygen sensor, you’ll need to diagnose the issue. The best way to fix this issue is to follow the factory recommendations for repairing the code. These instructions will allow you to fix the problem and get your car back on the road. If you don’t find any of these fixes online, you’ll want to seek out an experienced automotive mechanic to get the car back on the road as soon as possible.
While a DIY diagnostic tool can give you a rough idea of what the problem is, a more thorough examination will reveal whether the problem is an electrical problem or an internal engine issue. You can also check the condition of your exhaust system to see if it’s leaking or causing a smell. If your car is experiencing the P0430, you should check it out for any leaks or damage in your exhaust system. After fixing the exhaust system, you should test drive it to make sure it’s fixed correctly.
The catalytic converter itself is the main cause of the code P0430. When the catalytic converter isn’t performing optimally, it creates a generic fault code. If your catalytic converter is not working at a high enough level, the code P0430 will appear in the OBD-II diagnostic computer. If this is the case, your mechanic will have to replace the catalytic converter.
If you’re looking for a reliable P0430 diagnostic scanner, it’s worth investing in Carly’s universal OBD2 scanner. Compatible with all car brands with an OBD2 port, Carly will allow you to access your car’s data using your phone. Its mobile app will translate your data into insights, predictions, and possibilities, saving you time and money by identifying underlying problems. This means you can diagnose your car easily and affordably, which is something that every driver needs!
P0011
When you see a P0011 code on your dashboard, it means that your vehicle’s powertrain has a generic fault. The first digit is “0,” which means the fault is generic, and the second and third digits are the fault description. You must perform a pinpoint repair to fix the problem. To do so, you must use the manufacturer’s recommended pinpoint test. Performing the wrong test can damage your engine.
The diagnosis process should be followed according to manufacturer’s specific point-by-point procedures, to avoid misdiagnosis and replacement of parts that are still working. This will help you save money on parts and labor costs. Never replace a sensor without properly testing the component that is causing the problem. Once you have correctly diagnosed the problem, you can proceed to repair the vehicle. In severe cases, you may need to replace the entire component.
The P0011 error code is caused by a problem with the camshaft timing system. If your camshaft position ‘A’ in bank 1 is advanced, the problem will be reflected in the code. This can also be a result of a malfunction with your Nissan fixed valve intake operating angle. Alternatively, the camshaft actuator may leave the timing system as oil pressure changes. This may cause the P0011 code to appear on your dashboard.
There are several ways to prevent code P0011 from occurring in the first place. You should make sure to change your oil regularly and take your car to a mechanic for a checkup. Before you get to the P0011 code, you should address other fault codes. Low oil level, dirty oil, and sludge in the valve train may be the cause of the problem. In these cases, you may need to replace the engine.
There are many potential causes for the P0011 error. It could be due to old oil, low oil, or catastrophic engine failure. A technician who specializes in engine diagnosis and repair should be able to correctly diagnose the fault. The diagnosis fee usually ranges from $75 to $150. If you don’t have the time to do this, you can use a video to diagnose the problem. You will then know what the problem is and what repair methods will fix it.
You should also make sure that your vehicle has adequate fuel mileage to avoid a P0011 code. Low fuel mileage is another common cause. You might notice that your car runs rough or hesitates. The camshaft phasers are stuck in a position where they are too advanced. When this happens, your engine won’t get the right mix of fuel and air and may even fail the emission test. Fortunately, there are some simple diagnostic procedures you can do yourself.