You may have a problem with your vehicle’s transmission if you get an ob11 code. You can fix it by replacing the transmission or its related parts. In this article, you’ll learn about the most common causes of this code, and what to look for. You may also see an “8” for sensor failure. In addition to transmission problems, you’ll learn about EVAP and fuel metering systems.
O2 sensor
You might notice your car’s O2 sensor is malfunctioning when it displays a trouble code. If this is the case, you need to learn more about the codes to solve the problem. You can search the Internet for information on the codes P0130, P0131, P0036, P0137, and more. If you don’t have an OBD2 scan tool, you can get the information you need by reading online guides.
To replace an oxygen sensor, you need to take out the old one. Make sure the new one is threaded into the void left by the old one. There are special anti-seize compounds sold by Delphi that prevent the sensor from getting contaminated. Make sure you use the recommended amount of anti-seize as you don’t want to ruin the sensing area. Once you have the new sensor installed, you need to connect it to the diagnostic tool to erase the fault codes.
Oxygen sensors are located in the exhaust system and can become contaminated over time. Some of the reasons for contamination are too rich a fuel mixture, oil blow-by, or engine coolant. High temperatures also affect the sensor. It can lead to extended response times, a shift in the sensor voltage curve, and reduced performance. However, these are uncommon causes for the codes. If you suspect that your O2 sensor is faulty, take it to your mechanic immediately.
Regardless of the cause of your car’s O2 sensor trouble codes, a mechanic should always conduct diagnostics before replacing them. If the code is a P0135, for example, this means that there is a problem somewhere in the system. The same goes for the p0141 and p0135 codes. You’ll need to check your car’s diagnostics before you spend money on an expensive replacement.
The oxygen sensor in your car’s engine is one of the most important parts. It monitors the air/fuel ratio. By detecting the amount of oxygen in the exhaust stream, the ECM can adjust the fuel/air ratio. The O2 sensor in your car’s engine is located in the upstream position, just before the catalytic converter. Generally, there is only one bank, but “V” style engines have two exhaust sides.
Computer or output circuit fault
If you’ve ever stumbled upon one of these trouble codes, you’ve probably wondered where to start. While you may have the component itself to blame, the codes indicate the fault code associated with the circuit. A faulty computer output circuit or sensor could have a number of causes, including a wired connection to the car’s computer or upstream component affecting the ignition or fuel system. Besides faulty wires, other causes of a computer output circuit fault include electromagnetic interference and other sources.
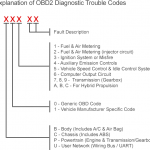
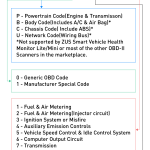
The first part of the code indicates the system, while the second character identifies the manufacturer. Then, the remaining digits are variable and relate to the specific problem. For example, if you see a P0500 code, your car may be experiencing a faulty computer. Alternatively, a P0600 code could mean your vehicle’s transmission computer is faulty. In this case, you will need to diagnose the problem with your car’s diagnostic tool.
Fuel or air metering system
An OBD-II trouble code will include the character “P,” which indicates a malfunction in the powertrain system. The second digit, “0,” indicates a generic code and the last digit indicates the specific fault code that is displayed. An OBD-II trouble code will display one of two symptoms: a fuel or air metering system malfunction or an ignition system problem. The first two symptoms indicate problems with the fuel metering system, while the latter describes an issue with the ignition system or auxiliary emissions control (ECU).
Depending on the code you receive, you might need to replace specific parts of the car. A faulty Mass Air Flow Sensor (MAC) may be the cause of the code. This component is responsible for ensuring that the engine gets the right amount of air. If the MAC is not functioning properly, the fuel/air mixture is not correct. In such a situation, the fuel/air mixture control system will compensate for the lack of air.
The P0171 code is a warning for a fuel-air mixture problem. If the mixture is lean, the engine computer will no longer be able to make up the difference between the air-fuel ratio and the air-fuel mixture. This causes a code to be set in the PCM, which stores a freeze-frame of parameters when the trouble code is set. The P0171 code is an indication that the short-term fuel trim adjustment has exceeded +25 percent.
EVAP system
If your car displays an EVAP system ob11 code, you may want to investigate the issue as soon as possible. This code can mean several different problems, and the correct solution will vary for each make and model. An EVAP system is designed to keep fuel vapors from escaping the engine and venting into the atmosphere. The EVAP system purges fuel vapors into the engine and monitors its sealing for leaks. If you have noticed that your car displays this code, you should check it out at the auto shop for a free quote.
EVAP problems aren’t always obvious to the average car owner, which is why it’s important to have a trained professional diagnose the problem.
In addition to a comprehensive diagnostic tool, your technician can also use a special “smoke” machine to locate leaks. This machine heats mineral oil to produce vapor-like smoke that can be detected by a UV leak detection dye. Self-tests can also be performed, but you will need a professional-level scan tool to cycle the purge solenoid and run the EVAP self-tests.
P0497 indicates that your EVAP purge flow is too low, preventing proper fuel combustion. In order to prevent this problem from arising, you should check for a blockage in the gas cap. In some cases, the problem can be as simple as a stuck purge valve. Depending on the vehicle, it may be possible to solve this issue by simply replacing the gas cap. However, you should check for all possible causes before you perform any repairs.
The main cause of EVAP error code P0455 is a leak. It happens when a fuel vapor leak sensor doesn’t provide enough airflow. If this problem isn’t addressed right away, you may experience a small decrease in fuel economy and the smell of fuel in closed spaces. If the problem isn’t solved quickly, it can also lead to increased emissions that pollute the air.