If you’re looking for an auto code reader, you’ve come to the right place. This article will walk you through the process of selecting a code reader, explains OBD-II codes and provides an overview of SAE codes. Regardless of your budget, you’re sure to find the best auto code reader that fits your needs. Read on to learn more! And remember that a code reader should not replace a mechanic.
OBD2 Scanner
If you are unfamiliar with OBD2 codes, you can start by reading the manufacturer’s list of codes. Then, plug your scanner into the OBD port to display the code information. Then, read the information on the display screen in English. Once you have determined which codes are causing your vehicle’s problem, you can proceed to diagnose the issue. The user manual will give you more information about the codes.
Some OBD2 scanners have a warranty of up to three years, but you should make sure it covers any repair work. Using an OBD2 scanner is an excellent way to save money on your car repair bill. Not only can you clear the system codes with a scan, but you can also troubleshoot problems like spark plug misfires and oil pressure. In addition, you can pull the vehicle’s identification number from its internal computer.
The OBD system was introduced in the early 1980s. Once it detected a malfunction, it turned on a check engine light and stored diagnostic trouble codes. Unfortunately, the codes were different for different auto manufacturers, making it difficult for mechanics to diagnose the problems in your car. In 1996, the OBDII standard was made mandatory for all cars. The OBDII standard specifies the type of diagnostic connector, electrical signaling protocols, and messaging format. Auto repair tools based on the OBD standard became more common.
OBD2 Reader
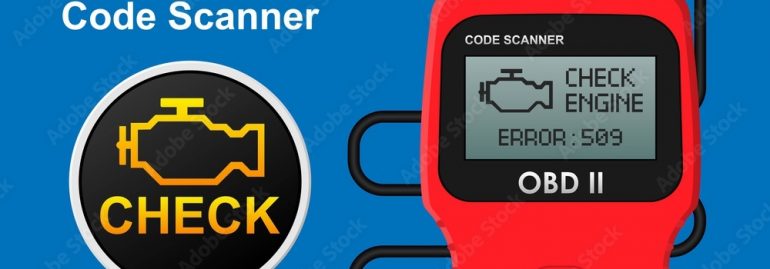
An auto code reader for OBD2 allows you to read trouble codes from your car’s computer and diagnose any problems. A professional code reader connects via wire to your car and can do practically anything the OBD2 standard can do. However, these scanners can cost hundreds, if not thousands, of dollars. That’s a big price tag for the average home mechanic. And if you want to avoid the high cost of diagnostic work, you can save even more money by doing daily diagnostics on your own.
The auto code reader for OBD2 is not only useful for displaying trouble codes, but it can also reset the check engine light. Some auto parts stores offer free code reading so you can get to know what’s going on inside your car. Most of the high-end scan tools come with an internal battery that lasts for hours. While there are several features to consider when choosing an auto code reader, you will most likely use its code lookup feature if you want to perform maintenance and repairs on your car.
The FIXD OBD2 scanner is a low-cost option that offers a host of benefits. It is easy to use and connects wirelessly to your car. The FIXD app provides helpful information and easy-to-understand explanations of trouble codes. The free app also offers helpful comparison information for your car’s maintenance. So, whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a car repair shop, you’re sure to find the right auto code reader for OBD2 in our list of recommendations.
OBD-II Codes
An OBD-II code reader can be extremely helpful in identifying a car’s malfunctions, but it’s not always easy to interpret the messages that the codes provide. These codes are typically grouped according to the component that’s failing. A pending code indicates a component problem, while an active code means a system failure. The P and U codes pertain to the same system, but they’re categorized differently. The P code covers the engine, transmission, fuel system, ignition, and emissions. The C code, meanwhile, covers the chassis, which covers the rest of the mechanical system.
OBD codes are classified into two groups: Active Codes and Pending Codes. Active Codes refer to malfunctions that keep the Check Engine light on, while Pending Codes are errors that occur at least once, but have yet to cause a vehicle to break down. When an error occurs, the auto code contains the necessary information for the car’s owners to identify the problem and take the appropriate action.
A diagnostic trouble code is a series of five letters and numbers generated by the onboard computer of a vehicle. These codes tell you which system is malfunctioning and what it’s supposed to do. The P0442 code, for example, indicates a leak in the evaporative emission system. There are hundreds of DTCs that can occur in today’s cars. An auto code reader can identify any of these and more.
SAE codes
An auto code reader that uses the SAE format is required by law in some countries. An auto code reader with this format must meet the specifications established by the manufacturer of the vehicle in question. It must also be compliant with the rules and regulations of the International Standard of Organization (ISO) and the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE). The first two organizations, ISO and SAE, have standardized the Diagnostic Trouble Codes and the methods for their interpretation.
There are two major categories of codes: body and chassis (B and C). B-codes refer to functions in the passenger compartment, while C-codes refer to functions outside the vehicle. The C-codes are generic codes, while P-codes pertain to the vehicle’s engine and transmission and their associated drivetrain accessories. The U-codes are manufacturer-specific codes. If you don’t know which code applies to your car, you should look for the manufacturer’s designation on the first digit of the trouble code.
Another type of code reader uses the OBD II standard. This means that it must be compatible with the OBD2 standard to work. A scanner can retrieve these codes and use them for troubleshooting. The first numeric digit specifies the type of code, while the second and third digits indicate a particular vehicle system. The last two digits indicate the type of fault the vehicle is experiencing. This means that a vehicle that does not meet these specifications is not safe to drive.
Manufacturer-specific codes
To determine which code your car may have, you should first understand what it means. This is an acronym for Diagnostic Trouble Codes, and is used by technicians and car owners alike. This diagnostic code identifies specific problems with your car’s engine. The first digit will tell you whether the code is generic or manufacturer-specific. There are many different DTCs, and knowing which one your car has can help you repair it.
Usually, the first character is the generic code. The second character will be the manufacturer-specific code. The next digit will tell you what part of the car is affected. Some examples of affected areas include misfiring and ignition, vehicle speed control, and the transmission. Using a manufacturer-specific code reader can be a lifesaver, so you can diagnose the cause of the issue quickly and efficiently.
Using a manufacturer-specific auto code reader can be an easy and affordable way to diagnose your car’s problems. It uses proprietary protocols instead of the standard OBD2 protocol. Auto diagnostic scanners can connect to all the modules in your car and pull fault codes that aren’t related to emissions. Some even allow you to reset the codes on your car. If you are unsure which code to look for, a dealer or technician can help you.
Diagnostic trouble codes
A diagnostic trouble code, or DTC, is a set of five-digit codes generated by the on-board computer management system of your vehicle. When a vehicle malfunctions, these codes can help the owner identify the underlying problem and determine the best course of action. These codes are defined by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), but some automakers also produce their own. If you need to diagnose your vehicle, you should know where to find the codes and where to look for them.
To find the right diagnostic trouble code, you need to know the exact meaning of each code. Some codes are generic, while others are more specialized and pertain to particular features of your vehicle. For example, if you’re trying to diagnose a transmission problem, you’ll need a “9” code. The “8” code, on the other hand, is a sensor failure. A diagnostic trouble code reader will help you determine which code you need to look for.
In a typical car, a diagnostic trouble code will consist of four digits and a letter indicating the system that the DTC belongs to. Each DTC has a corresponding description and may also come with a definition. A basic auto code reader will probably just give you the code number, but it will have a database specific to your car model. The more specific the DTC reader, the more accurate the diagnosis can be.