If you’ve ever experienced the frustration of trying to diagnose an OBD-II code on your car, you’re not alone. Whether you’ve gotten an annoying error message or you’re experiencing an obd code for the first time, you’ve come to the right place. In this article, you’ll learn how to recognize the symptoms of an OBD code and how to remove it. There are two ways to get the codes: one is easy and the other is complex. In either case, a scanner is your best bet.
OBD-II codes
OBD-II diagnostics used to be a niche industry for professional car mechanics. It was only diagnostic technicians who had the knowledge to read the check engine light codes. Today, however, anyone can read OBD-II codes with a simple diagnostic scanner. However, there are some limitations to OBD-II diagnostics. For starters, the codes cannot tell you what part of your car needs replacing.
In addition to repair information, OBD-II codes can tell you if your vehicle has an underlying problem. In fact, vehicle manufacturers have their own diagnostic software for their vehicles. However, these diagnostic systems can be complicated and confusing. To make them easier to understand, it’s helpful to refer to a list of commonly used OBD-II codes. The list below provides detailed descriptions and repair information for many common car problems.
It is vital to note that not all errors will trigger the check engine light. In some cases, seemingly unrelated problems may cause a lower priority code. Even cars with clean appearances can display misfire codes. Despite their apparent inconsequentiality, the codes should never be ignored. When a mechanic diagnoses a car, they need to know these trouble codes so they can quickly fix the problem. If you’re not sure what trouble codes your car has, check with the obd-ii trouble code chart.
If you’re not a technician, don’t worry! There are hundreds of OBD-II codes to learn about. Understanding these codes will make you more familiar with your vehicle, and prevent you from being sold unnecessary parts by unscrupulous “experts” at an auto parts store. They’re the worst of all. So, do yourself a favor and learn how to read OBD-II codes to know when you’re in need of repairs.
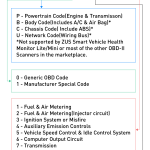
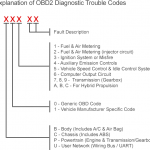
The main function of OBD-II is to monitor the performance of the engine and Emissions Control System. If something goes wrong with these systems, it will trigger the Check Engine Light. In most cases, a pending code will be followed by an active code. The codes are further divided into three categories: P – Powertrain – which deals with the engine, transmission, fuel system, ignition, emissions – and U – Network & vehicle integration. B – Body / Chassis – covers the vehicle’s mechanical systems, including the airbags, the steering wheel, the brake fluid and the axles. The last category is called Undefined and is a bit ambiguous.
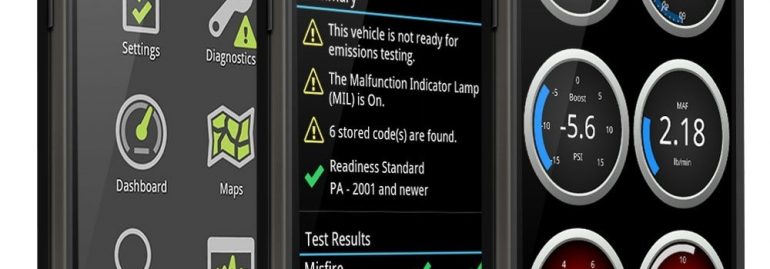
Code readers are an easy-to-use tool for reading OBD-II codes. They display the DTCs, but don’t provide a definition. The main downside to code readers is that they require manual entry, so they can’t be a substitute for an expert. However, if you’re looking for more advanced diagnostics tools, you can also use modern OBD scanners. These scanners are usually more expensive than basic OBD-II readers.
Symptoms of an obd code
In the United States, OBD codes have been identified as the cause of car problems and may be used to help diagnose engine problems. A diagnostic tool is a device that can read engine computers and identify the codes. There are several different types of codes, each with its own meaning. For example, a P0600 code could indicate a sensor issue, while a P0700 code would mean a TCM problem.
A P0201 code is an indication that a malfunction is occurring in the cylinder 1 injector circuit. The P0201 code indicates a problem with cylinder one of the injector circuit. The corresponding symptom is a check engine light. In many cases, a diagnostic scan will reveal the problem and suggest a fix. If you are unable to diagnose the problem yourself, visit a mechanic to fix it.
The P0171 code indicates that the fuel system is too lean (Bank 1). This is caused by too little fuel and too much air in the exhaust. Poor idle and low gas mileage can be attributed to this condition. The faulty MAF sensor, weak fuel pump, and failed fuel pressure regulator are other possible causes. Additionally, the O2 sensor itself can be the cause of the problem. A vacuum leak can also cause this code.
Another possible cause for the P0300 code is an engine misfire. A misfire can occur when the engine misfires repeatedly. The ignition timing may also be off. If this is the case, there could be a problem with the timing belt or chain. A car’s age can also affect compression levels. Loss of compression is the least common cause of P0300. Regardless of the cause, an OBD2 scanner should be able to diagnose this problem.
A P0122 OBD2 code means that the throttle position sensor (TPS) voltage is too low. This condition can occur when the engine is running for a number of minutes. Visual inspection can reveal loose or poor connections. Another cause for this code is a low voltage condition in the bank 1 sensor, or bank 2 sensor. In either case, a diagnostic scan can help pinpoint the problem. If you experience any of these symptoms, make sure to consult a professional.
How to remove an obd code
You may have a problem with your car and want to know how to remove an OBD code. Sometimes, the check engine light on your dashboard indicates that something is wrong with your vehicle, such as the anti-lock brakes or airbags. However, it can also mean that there is a problem with the transmission or emissions. Luckily, there are many things you can do to resolve the issue. Listed below are some tips and tricks to fix your car’s OBD codes.
To reset OBD1 or OBD2 codes, disconnect the negative (-) cable from the battery. The negative (-) cable is the one connected to the battery while the positive (+) cable is connected to the engine. The battery terminal is usually covered with a cap to protect it from moisture. Simply use a simple wrench to remove the cap. Don’t use a cutting wrench or screwdriver. The battery terminal should come together with two separate ends.