As modern vehicles become more advanced, so do the diagnostic tools used by automotive professionals. One such tool is the On-Board Diagnostics Version II (OBD II) system. This system allows mechanics and technicians to access valuable live data from a vehicle’s engine control module (ECM), providing crucial insights into its performance and overall health.
In this professional guide, we will explore the power of OBD II in reading live data, unveiling its potential for diagnosing issues, maximizing efficiency, and optimizing vehicle performance.
Whether you’re an experienced technician or simply interested in understanding the inner workings of your car better, this article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of how to effectively unlock the power of OBD II and harness its benefits for any automotive enthusiast or industry professional alike.
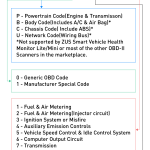
Understanding the Basics of OBD II: A Brief Overview
- Onboard Diagnostics (OBD) is a system installed in vehicles to monitor and report any issues related to their performance or emissions.
- The second generation of this system, known as OBD II, was introduced in the mid-1990s and has become standard in most cars since then.
- OBD II allows for easy access to real-time data from various sensors within the vehicle, providing valuable information for diagnosing problems.
How Does it Work?
- OBD II uses a standardized diagnostic port located under the dashboard, typically on the driver’s side. This port allows external devices such as code readers or scanners to connect with the vehicle’s computer system.
- When connected, these devices can retrieve codes that represent specific faults or malfunctions detected by onboard sensors. These codes help pinpoint potential issues within different systems like engine, transmission, or exhaust.
- The collected data can be interpreted using specialized software that translates numerical values into understandable readings such as RPM (revolutions per minute), coolant temperature, fuel trim levels, and more.
Why Is It Important?
-OBD II provides crucial insights into a vehicle’s health by detecting potential problems before they escalate further. -The ability to read live data allows mechanics and technicians to make accurate diagnoses quickly and efficiently based on real-time sensor readings. -A clear understanding of this technology empowers professionals with important troubleshooting capabilities while saving time and money for both themselves and their clients.
Navigating the OBD II System: Accessing Live Data
Accessing Live Data
Accessing live data from an OBD II system is a crucial step in diagnosing vehicle issues. It provides real-time information about the vehicle’s performance, allowing technicians to pinpoint problems accurately. Here are some key points to remember when accessing live data:
- Connect the OBD II Scanner: To access live data, you’ll need an OBD II scanner that connects to the vehicle’s diagnostic port. This port is typically located under the dashboard or near the driver’s side footwell.
- Power on and Select Vehicle: After connecting the scanner, power it on and select your vehicle make and model from its menu options.
- Retrieve Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Before accessing live data, it’s essential to retrieve any DTCs stored in the vehicle’s computer system. These codes provide hints about underlying issues affecting various systems within the car.
- Choose Live Data Parameters: Once DTCs have been retrieved, choose which specific parameters you want to monitor from a list provided by your OBD II scanner software.
- Interpret Real-Time Data: As you access these selected parameters in real time, interpret their readings against specifications provided by vehicle manufacturers or reputable repair databases.
Remember that interpreting this live data requires knowledge of typical values for each parameter based on manufacturer specifications – further highlighting why professional expertise is crucial for accurate diagnosis.
For more detailed steps on reading different live data parameters like engine speed, coolant temperature or oxygen sensor voltage etc., check out our comprehensive guide on “Unlocking Power of OBD-II”.
Conclusion
As technology continues to advance in vehicles’ diagnostic capabilities through onboard diagnostics version two (OBD-II), properly navigating its features becomes increasingly important for professionals tasked with repairing and maintaining cars efficiently and effectively.
By following these steps for accessing live data, mechanics and technicians can harness the power of OBD-II’s real-time information to diagnose problems accurately. This allows for faster repairs, reduced guesswork, and ultimately helps get vehicles back on the road safely.
Decoding Live Data: Interpreting PIDs and DTCs
Understanding PIDs: The Key to Live Data Interpretation
PIDs, or Parameter IDs, serve as codes that help decipher the meanings behind live data. These codes enable professionals to understand and interpret the wealth of information provided by OBD II systems. By referencing a PID chart specific to their vehicle’s make and model, technicians can identify which PIDs correspond to various sensors and components within the car.
To effectively analyze live data through PIDs, it is crucial for professionals to comprehend the range of values associated with each code. This understanding allows them to determine if recorded values fall within normal parameters or indicate potential issues that require further investigation. In essence, decoding PIDs not only offers insight into a vehicle’s current performance but also aids in early detection of malfunctions or abnormalities before they manifest into serious problems.
Decoding DTCs: Translating Malfunction Codes into Practical Insights
DTCs are Diagnostic Trouble Codes that provide invaluable information about detected problems in a vehicle’s system. Armed with DTCs retrieved from an OBD II scanner after conducting diagnostics on-board a car, mechanics gain access to specific error messages related to various components such as engine misfires, transmission failures, or emissions issues.
Interpreting these codes involves recognizing patterns and consulting reference materials such as technical service bulletins (TSBs) issued by manufacturers. With this knowledge at hand, professionals can pinpoint underlying causes contributing to malfunctions more accurately and efficiently troubleshoot electrical or mechanical breakdowns.
Mastering the art of decoding DTCs empowers automotive experts in diagnosing complex issues promptly and comprehensively – saving time for both themselves and their customers while ensuring vehicles’ optimal performance on the road.
Diagnosing Issues with OBD II: Troubleshooting Common Problems
Check Engine Light Illuminated
If the check engine light is on, it indicates that there is a problem in the vehicle’s systems. Using an OBD II scanner, you can retrieve the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) to get more information about the issue. These codes provide clues as to which component or system is malfunctioning and need attention.
Poor Performance or Stalling Engine
When your vehicle’s performance diminishes or if it stalls frequently, there may be underlying issues affecting its functionality. By checking live data using an OBD II scanner, you can monitor various parameters such as fuel trim levels, air-fuel ratios, and ignition timing. This allows you to identify any anomalies that could be causing the poor performance or stalling engine.
Unusual Sounds or Vibrations
Strange sounds or vibrations from your vehicle can indicate problems with specific components like the transmission or engine. By connecting an OBD II scanner and reading live data during driving conditions where these issues occur, you may be able to detect abnormalities in sensor readings related to those components. This valuable information enables you to pinpoint potential causes for investigation and repairs.
In conclusion, utilizing an OBD II scanner to diagnose common vehicle problems such as check engine light issues, poor performance/stalling engines, and unusual sounds/vibrations provides valuable insight into identifying and resolving underlying mechanical issues efficiently. It helps automotive professionals make accurate diagnoses by analyzing live data retrieved from sensors throughout the vehicle.
Maximizing Efficiency with OBD II: Using Live Data for Performance Optimization
Optimizing Fuel Economy
- Live data from OBD II enables precise monitoring of the vehicle’s fuel consumption and tuning the engine for optimal efficiency.
- By analyzing live data such as fuel trim, mass airflow rate, and oxygen sensor readings, mechanics can identify issues that impact fuel economy.
- Making adjustments based on this real-time data allows vehicles to maximize their fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
Improving Engine Performance
- With access to live data, mechanics can monitor critical engine parameters like ignition timing, throttle position, and air-fuel ratio.
- Evaluating these variables helps professionals diagnose problems accurately, ensuring engines perform optimally.
- Fine-tuning ignition timing or adjusting throttle position utilizing OBD II live data delivers improved horsepower, torque, and overall performance.
Extending Vehicle Lifespan
- Utilizing OBD II’s live data provides crucial insights into a vehicle’s health.
- Monitoring attributes such as coolant temperature, oil pressure, and transmission fluid conditions empowers mechanics to detect potential issues early on.
- By addressing minor problems promptly using accurate information from the onboard diagnostics system, unnecessary wear-and-tear is minimized—extending the lifespan of the vehicle.
The Future of OBD II: Advancements and Potential Applications
The field of On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) II is constantly evolving, bringing with it advancements that have the potential to revolutionize the automotive industry. With a deeper understanding of live data provided by OBD II systems, professionals can diagnose car problems more accurately and efficiently.
Advancements in technology have expanded the potential applications for OBD II. For instance, predictive maintenance could become a reality by analyzing real-time data from a vehicle’s sensors to identify issues before they lead to breakdowns or accidents. Additionally, researchers are exploring how OBD II data can be used for usage-based insurance programs, where safe driving habits are rewarded with lower premiums.
As technology continues to improve and new possibilities emerge, harnessing the power of OBD II will undoubtedly shape the future of automotive diagnostics and enhance both driver safety and convenience.