If you own a car, the first thing that you should do is to know how to read the OBD (On-Board Diagnostics) codes. There are many different codes you can look for. Some of them are generic and some are manufacturer specific. In this article, you will learn how to read each type of code. And, most importantly, how to avoid repairing your car with an inaccurate code. Hopefully, this information will help you.
OBD2 codes
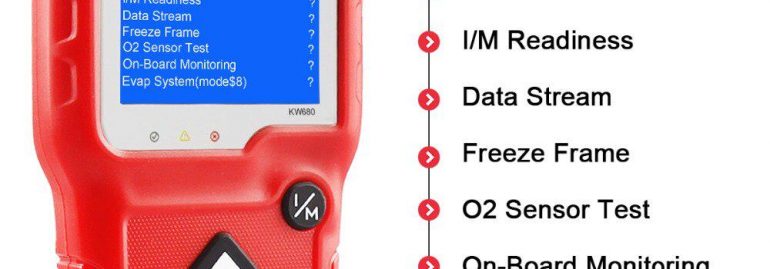
An OBD2 scanner can identify a variety of car trouble codes. These codes are assigned to different systems on a vehicle and contain a letter prefix and four digits. If you have a car that is using this technology, you can use these codes to troubleshoot the problem. The first digit of each code specifies the type of problem, the second indicates which system it belongs to, and the last two indicate the fault designation.
An OBD scanner uses a 16-pin trapezoidal connector to connect to a car’s OBD port, also known as the diagnostic link connector (DLC). OBD ports vary from vehicle to vehicle, but the majority are located beneath the driver’s side dashboard, near the pedals. If the port is located on the center dashboard or below the glove compartment, check the owners manual to find where the diagnostic link connector is located.
The check engine light may be confusing. A simple OBD reader can interpret these codes and help diagnose the problem. If the code is stored in the OBD memory, you can use a smartphone to diagnose it. An OBD reader will also provide an explanation. It will also allow you to perform troubleshooting without having to go to the car dealership. The car owner’s manual should be available online for easy reference.
In addition to troubleshooting the problem, an OBD2 scanner will show the vehicle’s engine status. This diagnostic tool can help you prevent future engine problems by clearing codes from the car’s computer. With the right tool, you can clear the check engine light and prevent any damage to your vehicle. OBD2 scanners are also useful for detecting other problems on the car, including oil pressure and spark-plug misfire.
Most diagnostic trouble codes are divided into four categories: chassis, engine, and body. The first category is called the standard fault code and covers all manufacturers. A generic code is P2xxxx, while a manufacturer-specific code is B3xxx. The last category, network and vehicle integration, covers systems shared with the car. When you’re using an OBD scanner, you can search online for codes and read descriptions of what they mean.
Generic OBD codes
There are more than three thousand generic OBD codes for cars. Most of these codes refer to a specific problem in a vehicle. Some of the generic codes are also called manufacturer-specific codes. The first digit of these codes indicates the type of fault and is unique to the particular vehicle make and model. The second digit indicates the type of the system the fault is related to. The last two digits identify the specific fault designation.
Diagnostic trouble codes are five-character strings that tell a vehicle is having a malfunction. A typical code has five characters. Each character represents a function: powertrain, chassis, body, and user network. Each of these codes has a unique definition and is managed by a manufacturer-specific computer. You can identify the specific trouble code by looking up the first digit. Once you have the code, you can begin the process of fixing the problem.
EVAP codes are used to identify issues with the vehicle’s EVAP system. EVAP is responsible for preventing gas fumes from entering the atmosphere and keeping air pollution to a minimum. Transmission codes monitor the car’s transmission, usually the transmission computer. These codes can be difficult to interpret without the proper tools. However, with the help of a good OBD scan tool, you can diagnose onboard vehicle problems with ease.
The main thing you should remember when dealing with OBD systems is to always bring your vehicle to a shop with the appropriate tools and knowledge. A good diagnostic reader will detect faults beyond DTC OBD codes. Using one is a good way to save money on repairs. You will be glad you did. Even if your car does not need an expensive repair, you’ll likely save money on the cost of labor.
While you can buy a generic OBD scanner and plug in the diagnostic cable, it will only provide a five-character code. You’ll need to consult the manual or the manufacturer’s website to understand what these codes mean. OBD scanners may be called ‘Codes’ or ‘Trouble Codes’ depending on their manufacturer. In most cases, a generic code reader will only provide a five-character code. The next step is to go to a website that provides complete OBD code definitions and fault alerts.
Manufacturer-specific OBD codes
When a car’s check engine light comes on, it may be an indication of a problem with the car’s engine management system, transmission, or another function. In these cases, a code called Diagnostic Trouble Codes, or DTCs, will be displayed. These are five-digit codes, one of which is the manufacturer-specific code, that identify a specific problem with the car. The codes are displayed on a scanner when the OBD system is connected to the vehicle. Each five-digit DTC is associated with a specific car problem.
The DTC is stored in the on-board computer of a vehicle. It is a code created in response to a malfunction in the car, or when the car’s sensors read values outside of their normal range. The purpose of the code is to guide a mechanic to the problem area, which may be causing the car’s dashboard indicator lights to malfunction. If you have a code that states ‘P0201,’ it means that there’s a problem in the injector circuit of the engine.
The OBD codes used in automobiles are typically divided into two categories, global and manufacturer-specific. The first category, powertrain codes, is devoted to engine and transmission functions, while the second category, U-codes, covers functions shared by computers and other systems. Some codes are universal, while others are specific to a particular manufacturer. General codes begin with 0 and apply to all cars manufactured according to OBD-II standards.
If you have this code, your next step is to reset it. Fortunately, this process is fairly simple and inexpensive. Using a simple OBD scanner can help you resolve the problem. If you want to know more about your car’s diagnostic codes, use the Carista app. These apps can be used to diagnose any on-board problems. It can also help you determine the causes of many problems with a car.
In most cases, a diagnostic trouble code consists of five characters. First, there’s the powertrain character (which represents the engine, transmission, and driveshaft), second, body, and chassis components, and third, the user network, which describes the functions managed by the car’s onboard computer. If the third character is a letter, it’s an indicator of a malfunction in the vehicle’s system.
How to read OBD codes
If you are a novice with cars, you may find it confusing to understand the trouble codes on your car’s computer. There are thousands of different OBD trouble codes. The good news is that if you can understand the codes, you can determine what’s wrong with your car. If you can’t read the codes, you can ask a mechanic to diagnose the problem for you. Here are a few things to look for in an OBD scanner:
A good place to start learning how to read OBD scanner codes for cars is by learning the types of problems that they indicate. For instance, an “8” code could mean the transmission is out of whack or has a sensor malfunction. The next letter, “9,” could indicate transmission-related issues. A “9” code would mean that a sensor isn’t working properly. These are just a few of the many different kinds of car trouble codes.
The next step in the process is to determine the exact cause of a check engine light. This light is a clear indication that something is wrong with the vehicle. Using an OBD scanner, you can determine what is causing it. Fortunately, most scanners will include the meaning of the codes for you. Using a code reader to check the car’s engine’s computer is a great way to save time and money.
OBD scanners come with a variety of tools that can help you diagnose the problem with a car. One of these is the OBD scanner. Using an OBD scanner to read a code will help you understand the problem in a vehicle. A car’s computer will often produce diagnostic trouble codes when it detects a problem. A P0201 code, for example, indicates that the MAF sensor has a malfunction in the injector circuit.
Another way to use an OBD scanner is with an Android device. For pre-1996 cars, an OBD scanner is necessary. The device has a Bluetooth connection. You will need a Bluetooth ELM/OBD/PLX adapter to connect to the vehicle. The best apps to read OBD scanner codes for cars are those that are compatible with an OBD2 port. If you have an iPhone, you can also download an app called Carly. These apps read the codes in real time and give you relevant information.