If you’re interested in learning more about Diagnostic trouble codes, this article will explain how to interpret them. We’ll also look at where to find the codes. Having trouble figuring out what obd i codes mean? Don’t worry, we’ll go over the most common ones, so you can make an informed decision. But before we do that, we should review some basic information about obd i codes.
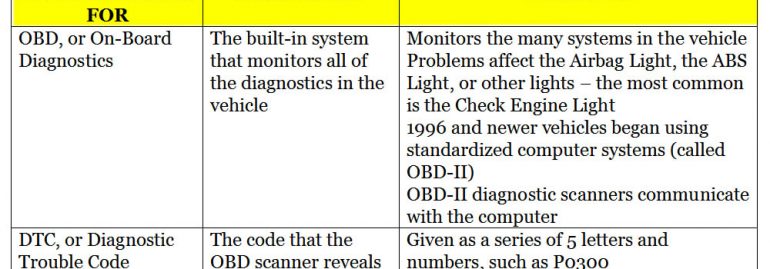
Diagnostic trouble codes
When your car or truck displays a diagnostic trouble code (DTC), the answer may be right in front of your nose. These codes are actually more of a guide than anything else, and they can help you diagnose and repair malfunctions in your vehicle. They’re also great for answering FAQs, like “Why is my car making these strange noises?” Luckily, most cars and light trucks in the US are OBD-II-compliant. Most heavy equipment, including diesel engines, also has these codes.
A diagnostic trouble code consists of five characters. The first two are powertrain, which is the engine and transmission. The third character stands for body, which refers to the passenger compartment. The fourth character, or “U,” represents the user network, which refers to the onboard computer. A diagnostic trouble code may contain a combination of these three characters. Typically, you’ll find three P codes, and one E code. The second set of codes are related to the emissions systems.
The next step in diagnosing a car problem is to identify the trouble code. Depending on the trouble code, it may mean many things. Some may be temporary, while others may not. But either way, it’s critical to diagnose the issue before it causes more serious damage to your vehicle. If you ignore diagnostic trouble codes, you may end up with a polluted vehicle or an unreliable engine. So, it’s best to keep an eye on them and take action if they appear. You’ll be glad you did.
Often, diagnostic trouble codes contain a third digit. A third digit defines a system that the trouble has occurred in. For example, a P0128 code may mean that the temperature of the engine’s coolant is too low to regulate the temperature. While this isn’t a manufacturer-specific code, it’s a generic code. It’s also possible to find a manufacturer-specific P0xxx code by checking for the manufacturer’s designation.
Your best bet is to consult the owner’s manual to confirm that your car’s DTC is OBD-II or J1939-compliant. If it isn’t, ask your dealership for advice. While DTCs can help you diagnose a car problem, they don’t necessarily mean what you need to replace. The wrong diagnosis could cost you thousands of dollars in repair bills. If the issue is not addressed quickly, your only option is to contact a professional.
Meaning of obd i codes
If you’re looking for answers on what obd i codes mean, you’ve come to the right place. The most common codes are grouped together in what’s known as a DTC code list. These codes are used by OBD2-compliant vehicles to help them identify the source of a problem and, if possible, repair it. There are two main categories of obd codes: type 1 and type 2. Both of them can be dangerous and may cause severe damage quickly, while type 2 codes can only create a freeze frame and have little impact.
The first category of OBDII codes is P. The letter P stands for powertrain, which covers the engine, transmission, and related accessories. The next category, U, covers the network & vehicle integration (NVI), which is handled by the onboard computer systems. The last category, C, covers all other mechanical systems on a vehicle. Each of these categories is organized by letter, and the codes begin with one of these letters.
You can learn more about what OBD codes mean by using a website that specializes in these codes. These websites also have videos that explain how to interpret the information contained in OBD codes. You can use an OBD scanner to check if a code is causing a problem, or if your car is just a general indicator of a malfunction. In addition to the aforementioned tools, you’ll need an OBD 1.5 compatible scanner.
When analyzing an OBD code, you’ll find that it contains information about the general cause of a lit Check Engine light. Each digit contains an error description. If your car’s Check Engine light is on, you can use the OBD Auto Doctor software to read the code and clear the check engine light. There are more than 18000 diagnostic trouble codes in OBD Auto Doctor’s database. You’ll be able to find the exact problem with your car by using this free software.
If the Check Engine Light is illuminated, you should take it to the mechanic. The car’s onboard diagnostics system records the malfunctions in your vehicle as unique codes. These codes are used to diagnose various issues with your car and are very useful for both mechanics and drivers. There’s no harm in checking your car, as long as it’s checked by a professional mechanic. Remember, though, that the Check Engine Light is only a warning light, and you should only diagnose a problem if you have an expertise in it.
How to read them
You might be wondering how to read OBD I codes on your car. OBD codes are a way to identify the general reason for your car’s Check Engine Light to come on. The codes are made up of letters and numbers, and the first two codes indicate the main problem. The fourth and fifth codes are paired numbers 00 to 99. Learn to recognize them and fix your car’s problems. Read on to discover how.
The first OBD code is ‘P’ for powertrain. This means the powertrain is malfunctioning, and it may need repair. The second code is ‘U’, meaning undefined. The list of generic codes for your car will be much longer than this. You can find the code that applies to your car by consulting the driver’s manual, or by searching the internet for a description. You may be able to fix the problem yourself with a simple diagnostic.
The third character is a digit that ranges from one to eight. The fourth character is a two-digit number, and the fifth character is a digit. The fault index represents the specific issue your vehicle has. The manufacturer’s manual will usually provide an explanation of the DTC, but you can use an intuitive and user-friendly tool to identify the trouble code. It takes a few minutes to learn how to read OBD codes, but you’ll find that it’s not as difficult as you may think.
The first step to learn how to read OBD codes is to understand the purpose of the ‘P’ code. While the purpose of ‘P’ is to help you identify the problem in your vehicle, OBD codes are actually a code that your vehicle has generated. This code is called a fault code, and is generated by your car’s on-board diagnostics system. An external device can communicate with your car using the OBD-II system, so learning how to interpret it can save you a lot of money.
After you have mastered this process, you can also use a professional scanner to get a full list of OBD codes. This way, you’ll be able to diagnose any issues that your car might be experiencing and can get your car back on the road. You can also use an online code reference to learn more about different codes. The best OBD scanner will have a list of codes on it. You can then choose the one that’s right for you.
Sources of obd i codes
OBDII codes begin with a letter. P stands for powertrain, which includes the engine, transmission and any associated accessories. P is also called a powertrain fault code. Similarly, U stands for network & vehicle integration, which controls onboard computer systems. Lastly, C stands for chassis, which refers to mechanical systems in the car. This type of code is more common than the others, but it still requires a proper diagnosis.
In general, OBD codes are a good way to identify the problem with a car. These codes are made up of a series of letters and numbers that indicate various issues. Some are single numbers like “P0201,” which means there is a problem with the cylinder 1 injector circuit. Other codes may be related to other problems in the car. However, they don’t always indicate the cause of the problem.
The data obtained from OBD-II is a valuable source of troubleshooting information. The process used for requesting diagnostic data is defined in the SAE J1979 standard. In addition, there is a list of standard parameters, or PIDs. These PIDs are identified by their own unique codes, and manufacturers aren’t required to implement all of them. Some manufacturers add proprietary PIDs.
OBD-II information can also be used for vehicle telematics and Pay-As-You-Drive insurance. OBD-II codes are generated by the OBD system, which consists of a series of five-character codes that can be translated into useful information for the owner. Once a vehicle’s OBD-II system detects a fault, the code can be used to determine the cause.